Kubernetes
Intro
- name?
- Always ask, ask anything
-
Can just follow, or do along
- Focus on asking questions instead
- Hard without multiple displays etc
- https://www.supervisor.com
- https://devopswithdocker.com/
- https://devopswithkubernetes.com/
- "The total workload of the course is about 95 hours."
- /docker.pdf
- /kubernetes.pdf
What is kubernetes
- kubernetes ~ google borg ~ 2014
In essence, Kubernetes is the sum of all the bash scripts and best practices that most system administrators would cobble together over time, presented as a single system behind a declarative set of APIs.
— Kelsey Hightower (@kelseyhightower) May 6, 2019
Or more officially:
“Kubernetes (K8s) is an open-source system for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. It groups containers that make up an application into logical units for easy management and discovery.” - kubernetes.io
A container orchestration system such as Kubernetes is often required when maintaining containerized applications. The main responsibility of an orchestration system is the starting and stopping of containers. In addition, they offer networking between containers and health monitoring. Rather than manually doing docker run critical-bank-application every time the application crashes, or restart it if it becomes unresponsive, we want the system to keep the application automatically healthy.
A more familiar orchestration system may be docker-compose, which also does the same tasks; starting and stopping, networking and health monitoring. What makes Kubernetes special is the robust feature set for automating all of it.
Kubernetes cluster
What is a cluster?
A cluster is a group of machines, nodes, that work together - in this case, they are part of a Kubernetes cluster. Kubernetes cluster can be of any size - a single node cluster would consist of one machine that hosts the Kubernetes control-plane (exposing API and maintaining the cluster) and that cluster can then be expanded with up to 5000 nodes total, as of Kubernetes v1.18.
See https://medium.com/paypal-tech/scaling-kubernetes-to-over-4k-nodes-and-200k-pods-29988fad6ed
We will use the term "server node" to refer to nodes with control-plane and "agent node" to refer to the nodes without that role. A basic kubernetes cluster may look like this:
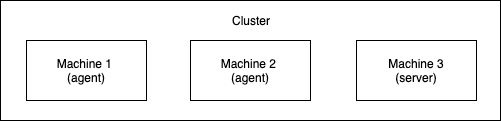
Where do I get one?
cloudnetes
-
- https://www.eksworkshop.com/
- https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/aws/amazon-elastic-kubernetes-service-adds-ipv6-networking/
- aws slow github issue https://github.com/aws/containers-roadmap/issues/1227
- https://github.com/aws/containers-roadmap/issues/724#issuecomment-1018497736
- https://docs.aws.amazon.com/eks/latest/userguide/create-kubeconfig.html
- https://docs.aws.amazon.com/eks/latest/userguide/kubernetes-versions.html
-
https://cloud.google.com/kubernetes-engine
- google $300 free credits
- https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/issues/69696
- https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/products/kubernetes-service/
- https://scaleway.com
- https://civo.com
- https://digitalocean.com
opsnetes
- https://registry.terraform.io/modules/terraform-aws-modules/eks/aws/latest
- https://gardener.cloud/docs/gardener/
localnetes
- Docker for Mac / Docker for Windows
- https://minikube.sigs.k8s.io/docs/start/
- https://kubernetes.io/docs/setup/production-environment/tools/kubeadm/create-cluster-kubeadm/
- https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kubespray
- https://github.com/k3d-io/k3d
mynetes
- https://k3s.io
- https://www.hetzner.com/ etc + k3s/k0s / kubeadm / kubespray
halfnetes
- https://www.scaleway.com/en/kubernetes-kosmos/
- https://aws.amazon.com/eks/eks-anywhere/
- https://cloud.google.com/anthos
- https://docs.aws.amazon.com/eks/latest/userguide/eks-outposts.html
Which one to choose?
- supporting services, databases, networks
- legal requirements
- business reasons
- credit reasons
- no reasons
Versions
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kubernetes -> Support windows
Memes
- https://twitter.com/memenetes/status/1576965336171175943
- https://twitter.com/jbogard/status/1566597167648833536
- https://twitter.com/memenetes/status/1181948714685992966
Why not setup run cluster on own machine?
That's what you can do later, now we can do stuff like autoscaling and distributed networking.